Furnace Heaters
Furnace heaters are critical components used in industrial furnaces that operate at high temperatures. These heaters play a crucial role in bringing the materials inside the furnace to the desired temperature in a short time. By doing so, they ensure that the materials in the furnace can stay at the required temperature for the necessary duration. Furnace heaters are widely used in industries such as steel production, ceramic manufacturing, lime production, cement manufacturing, and the glass industry.
These heaters are specially designed to meet the specific heating needs of various industries. In many production processes, materials must remain at a certain temperature for an extended period. Furnace heaters help maintain the desired temperature balance and ensure uniform heating inside the furnace, thus minimizing the risk of production errors.
Furnace heaters are typically made from special alloys that can withstand very high temperatures, ensuring long-term durability and consistent performance. These alloys not only provide electrical resistance to generate heat but also offer mechanical strength. As a result, furnace heaters do not experience significant wear or performance loss even after prolonged use. When heating materials inside a furnace, the heaters usually distribute heat evenly, helping to maintain a stable temperature balance, which is critical in industrial applications that require uniform heating.
Furnace heaters can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes depending on the specific needs of the industry. Different furnace types and production conditions require custom-designed heaters. For example, some furnaces require extremely high temperatures, while others operate at lower temperatures. Consequently, furnace heaters can vary in wattage, size, and shape to match the specific requirements of each furnace. This flexibility ensures that furnace heaters can be adapted to various production processes and furnace designs.
The correct selection of furnace heaters is essential for the efficient operation of the furnace. An incorrectly chosen heater may lead to temperature imbalances, which can affect the quality of the production. Moreover, it could result in increased energy consumption and higher operational costs. Therefore, industrial furnace operators must select the appropriate heaters based on the type of furnace and the production requirements. Factors such as temperature range, energy efficiency, durability, and performance must be considered when making this choice.
Additionally, furnace heaters may wear out or degrade over time, especially with heavy usage. Regular maintenance of these heaters is crucial to ensure they continue to function efficiently. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of the heaters and ensures that the furnace operates at peak performance. Maintenance tasks include cleaning the heaters, checking for proper functioning, and replacing them if necessary. Regular inspection of other furnace components is also important to enhance overall performance and prevent breakdowns.
Furnace heaters are not only used in industrial production processes but are also commonly found in laboratory furnaces and research facilities. In these applications, precise temperature control is often required, and furnace heaters can be designed to maintain these temperatures with high accuracy. These types of furnaces are usually smaller in scale and serve more specific production needs, while large industrial furnaces are optimized for high-volume production.
Furnace heaters are vital for ensuring the efficient and high-quality execution of industrial production processes. Customized for the specific conditions and requirements of each sector, these heaters provide long-lasting performance even under extreme temperatures and harsh operating conditions. For industrial furnaces to operate efficiently and achieve energy savings, it is crucial to select the correct furnace heaters and perform regular maintenance on them.
Industrial furnace heaters are used in furnaces that are used in the industrial
production phase. These products can do more than just heat. They can also melt
and cook. These products, which are also known as industrial furnace heater,
operate on different principles depending on their intended use. In other
words, we can provide constructive solutions to your needs with furnace heaters
tailored to various industries.
Technical Specifications of Furnace Heaters
- Furnace heaters are capable of operating at high temperatures up to 1400 degrees Celsius. This ability allows them to meet the high-temperature requirements of industrial production processes.
- These furnaces facilitate the processing of industrial materials that undergo chemical reactions. They are particularly useful in metalworking, ceramic production, glass manufacturing, and other high-temperature industrial processes.
- Heaters with a working capacity higher than 400 degrees Celsius are classified as furnace heaters. These heaters are used in furnaces that require high temperatures and can operate efficiently for long periods.
- The heating process in furnaces begins when thermostats send electrical signals to the relays inside the furnace. This ensures precise temperature control, allowing the furnace to function efficiently and maintain the desired temperature.
- Furnace heaters can operate at high performance for many years under challenging conditions. When a component malfunctions, part replacement is usually recommended to restore the heater's original performance.
- Furnace heaters are made from materials such as metal wire and carbon. These materials provide high thermal resistance and electrical conductivity, ensuring the heater performs efficiently even under high temperatures.
- Furnaces use different types of heaters based on temperature ranges: tube-type heaters for up to 500°C, spiral wound heaters and radiant tube heaters for up to 1300°C, silicon carbide heaters for up to 1400°C, and molybdenum disilicide heaters for up to 1700°C. This variety of heaters provides tailored solutions for furnaces operating in different temperature ranges.
Applications of Furnace Heaters
Furnace heaters are widely used in industrial production sectors. In industries such as glass manufacturing, ceramics, and metalworking, furnaces are required to melt or shape even the highest metals. These furnaces rely on heaters to achieve the high temperatures necessary for these processes. In industrial furnaces, heater systems play a critical role, not only providing heat but also enabling the furnace to operate at the high temperatures required for these production processes.
Furnace heaters are also used in industrial kitchens. In kitchens with high-volume production, heaters provide an efficient and reliable solution for heating and cooking. Industrial kitchens, especially those in large-scale restaurants and catering businesses, rely on furnace heaters to manage the high demands of food preparation. These furnaces are ideal for businesses seeking compact equipment that doesn’t take up much space but still delivers excellent performance. Furnaces with built-in heaters are indispensable for ensuring high-quality food preparation in commercial kitchens.
In industrial kitchens, furnace heaters not only perform cooking tasks but also help maintain the desired temperature for food storage. This feature is crucial in ensuring food is served at the optimal temperature. Additionally, kitchens that aim to make the most of limited space will benefit greatly from compact, high-efficiency furnace heaters. These devices can also be adapted to meet specific requirements based on the restaurant’s menu and production capacity. The ability to control temperatures digitally adds to the user-friendly experience of these kitchen appliances.
Moreover, furnace heaters are commonly used in laboratory and research facilities. In these environments, precise temperature control is often necessary, and furnace heaters can be designed to meet these needs with great accuracy. Laboratory furnaces used for material analysis, heat treatment, or experimental heating processes require stable and high temperatures. Furnace heaters are ideal for these applications due to their high thermal resistance and reliable performance even at elevated temperatures.
In conclusion, furnace heaters are essential in both industrial production processes and specialized sectors like industrial kitchens and laboratories. With their high-temperature resistance, energy efficiency, and long-lasting performance, these heaters contribute to the overall efficiency and quality of production. By selecting the right furnace heaters and performing regular maintenance, businesses can ensure that their production processes remain seamless and cost-effective.
What Are the Advantages of Furnace Heaters?
One of the most important advantages of furnace heaters is that they allow production to take place quickly and in large volumes. In environments where high temperatures are required, they enable precise control of the material. Processing and controlling a material at high temperatures is a very challenging process, but furnace heaters make this task easier by ensuring materials reach the desired temperature quickly and efficiently. This results in more efficient production processes and minimizes time and cost losses for businesses. In addition, the high-temperature requirements are met, allowing for faster and higher-quality production.
Furnace heaters not only provide temperature control but also contribute to energy efficiency. Industrial furnaces, with their efficient heating methods, help save energy and reduce operating costs for businesses. This energy saving positively impacts the business's budget and reduces environmental impact. High-efficiency furnace heaters minimize energy losses, creating a more environmentally friendly production process.
Another advantage of furnace heaters is their long lifespan and durability. In industrial production processes, furnaces are constantly exposed to high temperatures and heavy usage. However, high-quality furnace heaters can work safely and efficiently for many years. This ensures businesses can continuously use high-performance furnaces, reducing maintenance and repair costs in the long term.
Furnace heaters can be customized to meet the specific needs of different industries. Depending on the type of furnace and process requirements, the size, shape, and heating capacity of the heaters can be adjusted. This flexibility ensures optimal performance in any industrial process. For example, in sectors like glass manufacturing, where high temperatures are essential, specially designed furnace heaters can be used. These customizations help achieve maximum efficiency at every stage of the production process.
Additionally, when properly maintained, furnace heaters offer a long service life. Regular maintenance ensures that furnace heaters continue to operate at peak efficiency and prevents wear. Periodic maintenance helps prevent malfunctions and reduces repair costs. This ensures business continuity while lowering operational costs in the long run.
Furnace heaters also offer significant safety advantages. Modern furnaces are equipped with high-temperature control systems and safety mechanisms. This feature helps businesses minimize safety risks during production processes. The durable construction of furnace heaters helps prevent overheating or malfunctions, creating a safe working environment. This ensures both the safety of employees and minimizes potential production interruptions.
In conclusion, furnace heaters allow industrial production processes to occur quickly, efficiently, safely, and cost-effectively. The advantages they provide in terms of both time and energy enhance operational efficiency for businesses. Additionally, their long lifespan and customizable features offer solutions for every type of production need. For this reason, furnace heaters are an indispensable part of modern industrial production processes.
Furnace Heaters Prices
Furnace Heater prices vary according to the size, technical features,
and functions of the product. Our customers place
orders for various products based on the area and volume of business in their
manufacturing facilities. That is why, rather than providing a firm price
offer, we first learn about your requirements. We prepare a price offer for you
after learning about your requirements. You can contact us right away for
information and advice on furnace heater. Furthermore, our team can come to
your home and conduct a free discovery. We complete the production of the
furnace heater that we have specially designed for you in a timely manner, and
we make every effort not to disrupt your production process
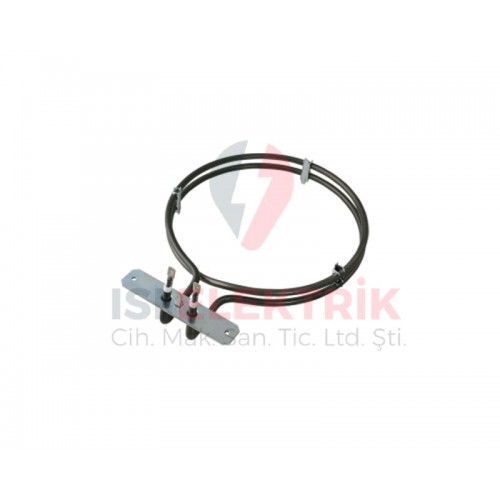
Heater Elements for Furnaces
Heater elements, also known as furnace heaters, are electric devices found inside furnaces that generate heat to cook food. Heater elements can be found at the bottom, top, or both sides of the furnace.
Heater elements come in two main types:
- Bottom Heaters: Bottom heaters are located at the bottom of the furnace and are used to cook the bottom part of the food.
- Top Heaters: Top heaters are located at the top of the furnace and are used to cook the top part of the food.
Furnace Heater Types
- Ceramic Heaters: Ceramic heaters are made from ceramic materials that are highly resistant to high temperatures. These heaters are typically used to better distribute heat within the furnace. Due to their excellent thermal properties, ceramic heaters can withstand rapid temperature fluctuations and prolonged exposure to high temperatures without degrading. They are commonly used in industrial applications where uniform heating and long-lasting durability are critical. Ceramic heaters are ideal for processes that require precise temperature control and consistent performance over time.
- Quartz Heaters: Quartz heaters are known for their rapid heating and cooling characteristics, making them an ideal choice for industries that require quick temperature changes. Quartz is resistant to high thermal stresses, meaning these heaters can withstand extreme heat without losing performance. They are often used in furnaces where fast temperature response times are crucial, such as in glass manufacturing, ceramics, and various heat-treatment processes. Quartz heaters offer excellent durability and efficiency, making them reliable in high-temperature environments.
- Semiconductor Heaters: Semiconductor heaters are commonly used in industrial furnaces, particularly in specialized applications that require precise temperature control and high heat resistance. These heaters are made from semiconductor materials that offer controlled heat generation properties. Semiconductor heaters are designed to handle extremely high temperatures and are often tailored for specific processes, such as special baking requirements or precision heating in research and development environments. The ability to adjust the resistance allows for fine-tuning of the temperature, making them suitable for more sensitive or complex heating tasks.
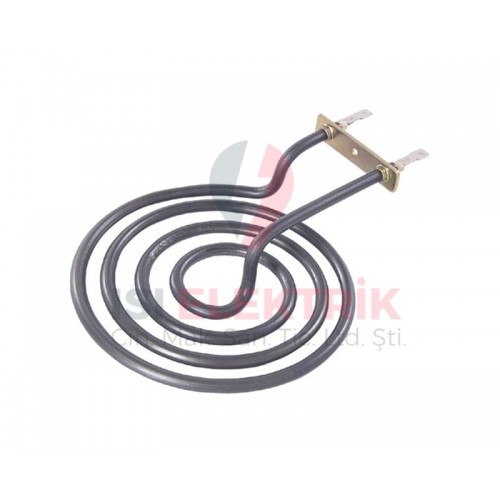
- Spiral-Wound Heaters: Spiral-wound heaters are designed to provide even heat distribution through their coiled structure. The design allows for maximum surface area contact with the air or material inside the furnace, ensuring efficient heat transfer. These heaters are ideal for high-temperature industrial applications and are often used in processes like metal heat treatment, glass production, and ceramics. Their robust construction enables them to handle extreme conditions, making them highly durable for prolonged use.
- Silicon Carbide Heaters: Silicon carbide (SiC) heaters are used in high-temperature environments due to their superior resistance to heat and thermal shock. These heaters are widely used in furnaces that reach temperatures exceeding 1400°C. Silicon carbide's ability to withstand extreme thermal conditions makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications such as metal smelting and high-temperature furnaces in research labs. SiC heaters offer long service life and excellent thermal efficiency, reducing energy consumption while maintaining high performance.
- Molybdenum Disilicide Heaters: Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heaters are designed for the most demanding high-temperature applications. With the ability to operate at temperatures as high as 1700°C, these heaters are used in furnaces that require precise control at extreme heat levels. MoSi2 heaters are particularly valuable in industries like semiconductor processing, metal forging, and high-performance materials testing. These heaters provide stable, long-term performance and are well-suited for environments where consistent and reliable heating is essential.
- General Technical Specifications:
- Power: Available in different power levels ranging from 500 watts to 3000 watts.
- Electric Voltage: 220 volts or 240 volts.
- Temperature Range: Can be used within various temperature ranges from 50°C to 500°C.
- Diameter: Available in various diameters ranging from 8 mm to 20 mm.
- Length: Available in different lengths ranging from 100 mm to 1000 mm.
- Body Material: Can be made of various materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or cast iron.
- Heating Element Material: Can be made of different materials such as nickel-chromium, stainless steel, or Inconel.
- Protection Class: Available in different protection classes such as IP20, IP44, or IP65.
- Connection Type: Available in different connection types such as butterfly nut, cable connection, or plug connection.
- Other Technical Specifications:
- Heating Speed: How quickly the heater element heats up.
- Cooling Speed: How quickly the heater element cools down.
- Heat Distribution: How the heater element distributes heat.
- Lifespan: How long the heater element can last.
- Flexibility and Variety: Furnace heater elements can be produced in different sizes, shapes, and power levels, providing solutions suitable for different types of furnaces and application needs.
- Homogeneous Heat Distribution: Quality furnace heater elements provide homogeneous heat distribution inside the furnace, ensuring that food or processed materials are cooked or processed evenly.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: Electric furnace heater elements produce fewer carbon emissions compared to furnaces that operate with natural gas or coal, contributing to reducing environmental impact.
- Easy Installation and Maintenance: Furnace heater elements generally require easy installation and maintenance. When replacement is needed, removing the old heater element and installing a new one is usually straightforward.
- Less Odor and Smoke: Electric furnace heater elements produce less odor and smoke compared to furnaces that operate with gas or coal. This improves indoor air quality and provides a more comfortable atmosphere in workplace or home environments.
- Body Material:
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is the most commonly used body material for furnace heater elements. It is durable, corrosion-resistant, and easy to clean.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion. It is less commonly used in furnace heater element production.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron is sturdy and durable. It is less commonly used in furnace heater element production.
- Heating Element Material:
- Nickel-Chromium: Nickel-chromium is the most commonly used heating element material for furnace heater elements. It is durable, can withstand high temperatures, and has a long lifespan.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is corrosion-resistant and easy to clean. It is less commonly used in furnace heater element production.
- Inconel: Inconel is resistant to high temperatures and corrosion. It is an expensive material and is used in special furnace heater applications.
- Insulation Material:
- Ceramic: Ceramic can withstand high temperatures and provides good insulation. It is the most commonly used insulation material in furnace heater element production.
- Mica: Mica can withstand high temperatures and is flexible. It is less commonly used in furnace heater element production.
- Connection Elements:
- Butterfly Nut: Butterfly nuts are used to secure the furnace heater element to the furnace.
- Cable Connection: Cable connections are used to connect the furnace heater element to the power source.
- Plug Connection: Plug connections are used to easily attach and detach the furnace heater element.
- Technical Details to Consider When Selecting Furnace Heater Elements
- Power: The power of the heater element should be chosen according to the size of the furnace and the intended use. Larger furnaces require more powerful heater elements.
- Voltage: The voltage of the heater element should match the voltage of the furnace's electrical system.
- Temperature Range: The temperature range of the heater element should be selected based on the foods to be cooked. Different cooking processes require different temperatures.
- Body Material: The body material of the heater element should be selected according to the environment inside the furnace. Stainless steel is the most common choice due to its resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning.
- Heating Element Material: The heating element material should be heat-resistant and long-lasting. Nickel-chromium is the most commonly used heating element material in furnace heater elements.
- Protection Class: The protection class of the heater element should be chosen according to the environment inside the furnace. Heater elements that provide protection against factors such as water and dust should be preferred.
- Connection Type: The connection type of the heater element should be selected according to the model and brand of the furnace. Different connection types, such as butterfly nuts, cable connections, or plug connections, are available.
- Size: The size of the heater element should be suitable for the interior of the furnace. The heater element should have sufficient space inside the furnace and should not come into contact with the food.
- Additional Features: Some furnace heater elements come with additional features such as thermostats, timers, or cooking programs. These additional features can make the cooking process easier and more controlled.
Technical Specifications of Furnace Heater Elements
Advantages of Furnace Heater Elements
Materials Used in Furnace Heater Element Production
Technical Details to Consider When Choosing Furnace Heater Elements
Furnace Heater: Features Providing High Heat Efficiency
Furnace heaters are critical components used in modern industrial production processes to enhance energy efficiency, optimize temperature control, and deliver high performance. In industrial furnaces, which are essential for various heating applications, the heater elements are designed to withstand high temperatures and ensure durability for long-term usage. Furnace heaters are particularly beneficial in industrial furnaces as they help optimize energy consumption, reduce heat loss, and increase efficiency. By providing high heat efficiency, these products allow for lower electricity consumption while reaching higher temperature levels with ease.
The heat efficiency of furnace heaters is one of the most important characteristics in their design. A highly efficient furnace heater minimizes energy loss by distributing heat evenly, which not only saves energy but also speeds up the heating process, helping improve production timelines. In industrial furnaces, these features enable faster reaching of the desired temperatures and significantly reduce energy costs. Furnace heaters with superior heat efficiency also provide an eco-friendly solution by helping businesses reduce their carbon footprint.
The high efficiency of furnace heaters is directly related to the quality of the materials used and the specialized design of the heating elements. High-quality materials such as stainless steel, nickel, and chromium alloys provide both high temperature resistance and long-lasting performance. These materials ensure that furnace heaters maintain temperature stability and transfer heat rapidly. Additionally, the use of innovative technologies in heater design not only boosts heat efficiency but also guarantees long-term performance for a variety of industrial applications.
Technical Details
The technical characteristics of furnace heaters can be customized to meet specific requirements for each application. These features range from the materials used to the design, power ratings, and installation methods. First and foremost, the power ratings of furnace heaters determine the amount of energy they consume, and selecting the right power is crucial for ensuring the system operates efficiently. Typically, furnace heaters are designed to operate at specific wattage levels, and this rating is determined based on the temperature needs of the application.
The operating temperatures of furnace heaters vary depending on the type and quality of the alloys used. For example, nickel alloys, which have high-temperature tolerance, are preferred for furnace heaters that operate up to 800°C, while alloys with lower thermal capacity are used in furnaces operating at lower temperatures. The temperature resistance of furnace heaters is also closely related to their wear resistance. Wear is a significant factor in systems operating at high temperatures for extended periods, so furnace heaters must be durable and long-lasting to ensure reliable operation in industrial applications.
Another important technical feature is the heating speed of the furnace heaters. High-quality furnace heaters heat up quickly and reach the desired temperature levels faster. This accelerates production processes and shortens operational times. Additionally, the ability of furnace heaters to maintain stable temperature control and provide uniform heating ensures that products always meet the same quality standards. This is particularly important in industries that require precise production processes.
Furnace heaters also offer energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions. Thanks to innovative designs, unnecessary energy loss is prevented, and more heat is generated with less energy. This reduces operating costs for businesses and provides an environmentally conscious manufacturing process. Furthermore, the eco-friendly design features contribute to the manufacturer’s ability to obtain environmental certifications such as ISO 14001.
Lastly, the installation and maintenance of furnace heaters are relatively simple. Most industrial furnace heaters are designed for user-friendly installation and maintenance, minimizing downtime and ensuring that equipment operates at peak efficiency at all times. This allows businesses to reduce production interruptions and maintain optimal performance of their systems.
Furnace Heaters Technical Details to Consider When Choosing
- Power Capacity: The wattage of furnace heaters should be sufficient to meet the heating requirements of the furnace. A heater with inadequate power capacity may operate inefficiently, leading to longer heating times and higher energy consumption.
- Operating Temperature: Furnace heaters are designed to operate within a specific temperature range. It is important to choose a heater that can handle the maximum temperature required by the furnace. If the selected heater is not capable of operating at the necessary temperature, it may wear out prematurely and operate inefficiently.
- Material Quality: Furnace heaters are made from alloys that can withstand high temperatures. Alloys such as stainless steel, nickel, and chromium have the ability to transfer heat rapidly and provide long-lasting performance. Material quality directly affects the durability and reliability of the heater.
- Dimensions and Easy Installation: The dimensions of the furnace heater should be compatible with the installation space. Easy installation contributes to faster maintenance and repair processes, enhancing operational efficiency.
Furnace Heaters Operating Principle
Furnace heaters work by converting electrical energy into heat energy. The operating principle involves passing electric current through a resistive material. The current is resisted by the material, and this resistance generates heat. The electrical current flows through the high-resistance alloys in the heater element, which converts the energy into heat, thereby increasing the temperature in the furnace. This mechanism allows the heating system to function efficiently and effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Furnace Heaters